When companies consider SOC 2 compliance, they often think of it as an external requirement — something they need to win deals with larger clients or meet industry expectations. While that’s true, SOC 2 is more than just a security certificate. At its core, it’s a framework designed to help organizations handle data responsibly through a set of guiding standards called the five trust service principles.
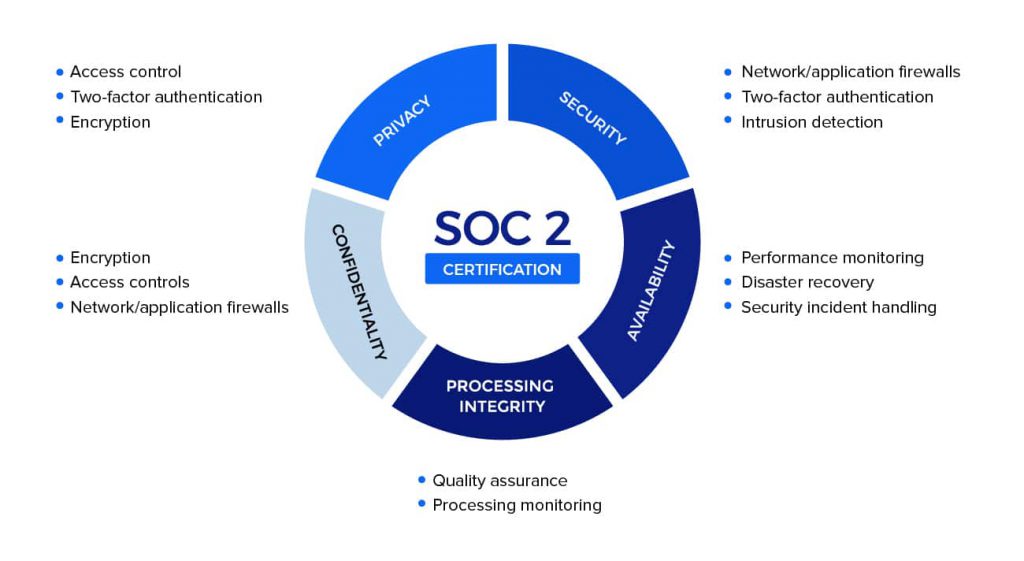
These principles — security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy — form the backbone of SOC 2 audits. Each one targets a different dimension of risk and ensures your company takes a holistic approach to safeguarding sensitive data. Understanding these principles not only makes compliance less intimidating but also highlights how they create real, measurable business benefits.
The first and most important trust principle is security. It ensures that your systems are safeguarded against unauthorized access, whether from external attackers or internal misuse. To meet this principle, businesses implement measures like firewalls, multi-factor authentication, encryption, and continuous monitoring.
Business Impact: Security is the foundation of customer trust. By meeting this standard, companies can prevent costly breaches, reduce downtime, and assure clients that their data won’t end up in the wrong hands. This directly supports sales conversations, where prospects want proof of strong safeguards before they sign on.
2. Availability: Keeping Systems Reliable and Accessible
The availability principle focuses on whether systems and services are operational and accessible as promised. It doesn’t just look at uptime but also at the processes in place to handle unexpected disruptions — like disaster recovery planning and incident response protocols.
Business Impact: Customers today expect 24/7 access to digital services. A SOC 2-compliant organization demonstrates that it has the infrastructure, backups, and monitoring to keep systems running smoothly. This reliability boosts customer satisfaction and helps avoid reputational harm from outages.
3. Processing Integrity: Ensuring Accuracy and Completeness
Processing integrity ensures that a system processes data accurately, completely, and in a timely manner. This principle applies to businesses that handle sensitive or transactional data — from billing platforms to SaaS providers managing client workflows.
Business Impact: Mistakes in data processing can lead to billing errors, reporting issues, or compliance violations with other regulations. By adhering to this principle, businesses minimize costly errors and prove to customers that they can deliver consistent, accurate results.
4. Confidentiality: Safeguarding Sensitive Information
Confidentiality ensures that sensitive business information — such as trade secrets, intellectual property, or client contracts — is properly protected. Companies demonstrate compliance by implementing data encryption, access restrictions, and secure data disposal methods.
Business Impact: For industries like healthcare, finance, and technology, protecting confidential data is critical to maintaining client relationships. Meeting this principle reassures customers that their sensitive information is safe, which is often a deciding factor in vendor selection.
5. Privacy: Respecting Personal Information
The privacy principle focuses specifically on the collection, use, retention, and disposal of personal data. While confidentiality deals with business data, privacy zeroes in on customer and employee information. SOC 2 ensures that organizations follow clear policies aligned with modern privacy expectations and regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Business Impact: In a world where consumers are increasingly aware of how their data is used, demonstrating strong privacy practices builds brand trust. Businesses that meet this principle reduce the risk of regulatory fines while showing customers they respect their personal rights.
Why the Principles Matter for Your Business
What makes SOC 2 unique is its flexibility. Not every organization is audited against all five principles — instead, the ones most relevant to your business are selected. For example, a SaaS company might prioritize security, availability, and confidentiality, while a payroll processor may need to focus on processing integrity and privacy as well.
This tailored approach means businesses aren’t just meeting arbitrary rules. They’re aligning compliance with the specific risks and expectations of their industry, clients, and operations.
Final Thoughts
The five trust service principles are more than an audit checklist — they are a blueprint for building secure, reliable, and trustworthy businesses. By embracing these standards, companies don’t just achieve SOC 2 compliance; they also strengthen their operations, earn client confidence, and reduce risks that could threaten growth.
In short, SOC 2 compliance is not just about “getting the certificate.” It’s about proving, through a well-established framework, that your business is built to handle sensitive data responsibly and deliver consistent value to your customers.
